What makes a great organization great? Is it only about a solid strategy, great planning, and exceptional execution, or is there more to it?
What truly separates organizations that achieve greatness and happy workers, from those that stall out?
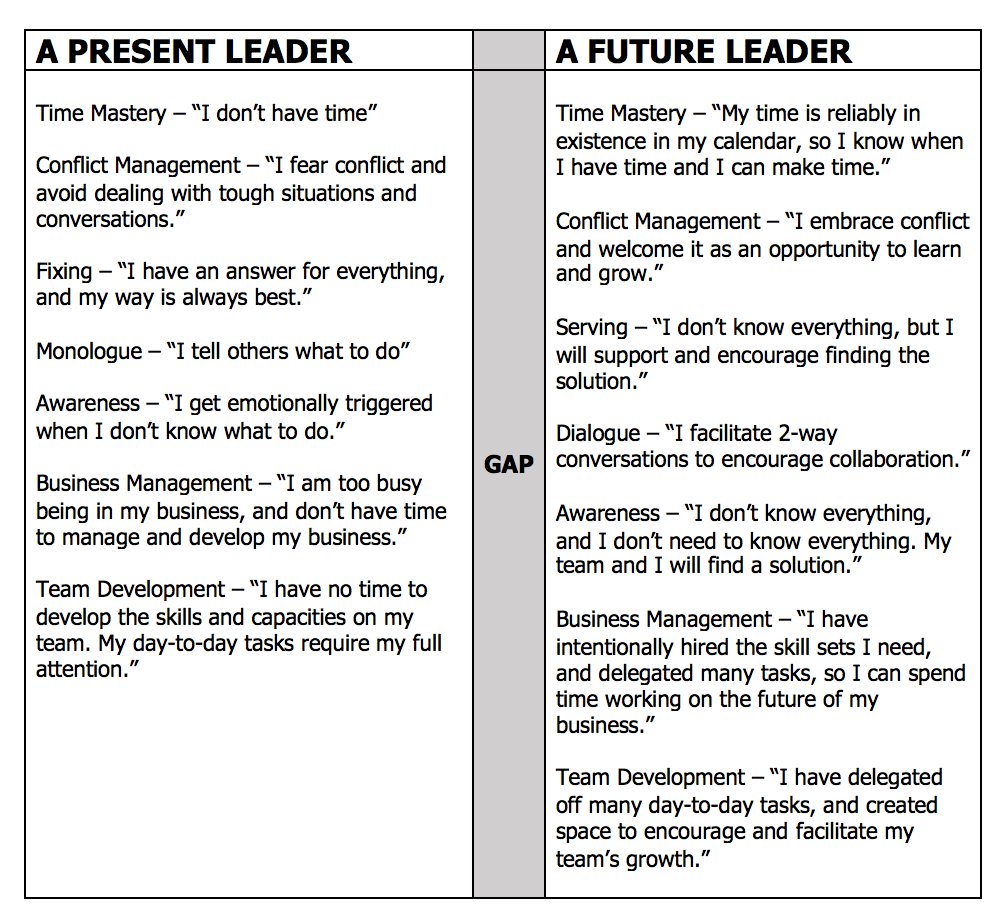
Many organizations spend a great deal of time hammering out their vision, mission, core values, strategy, and plan for execution. All these items are necessary and very important, but what is often missing in these plans are the plans for how to ensure the team is set up properly to execute with excellence.
What does this mean?
Does the organization have the culture, communication, support structures, processes, and agreements to effectively execute on the plan? Does the team effectively communicate with each other and know how to work well together to be productive?
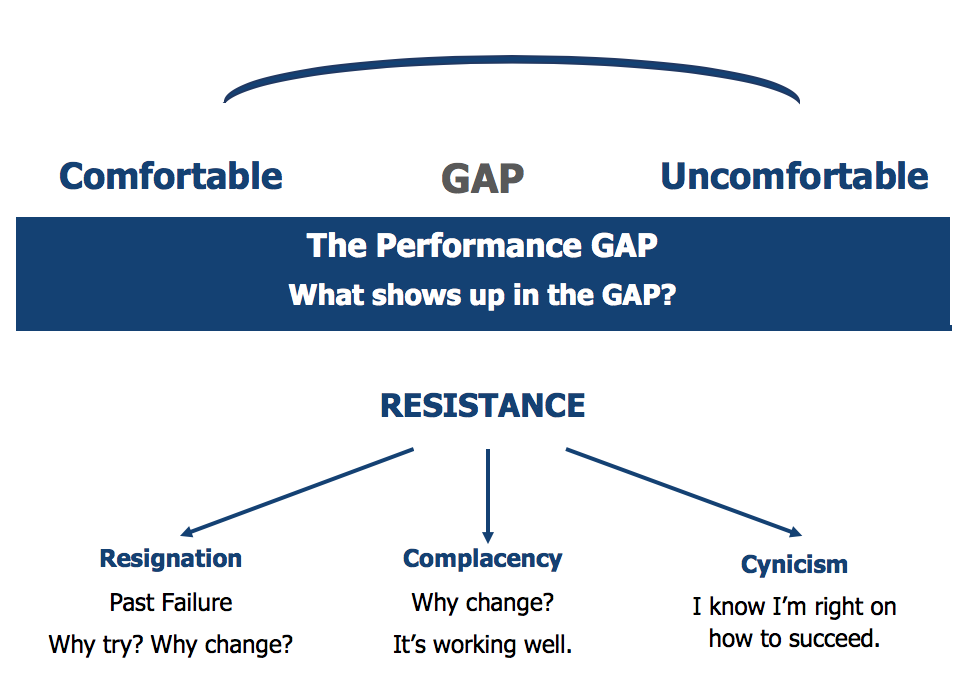
Basically, what is the level of “Workability” in your organization?
At the end of the day, people are the ones doing the work, therefore they need to know how to work well together to achieve the organization’s goals.
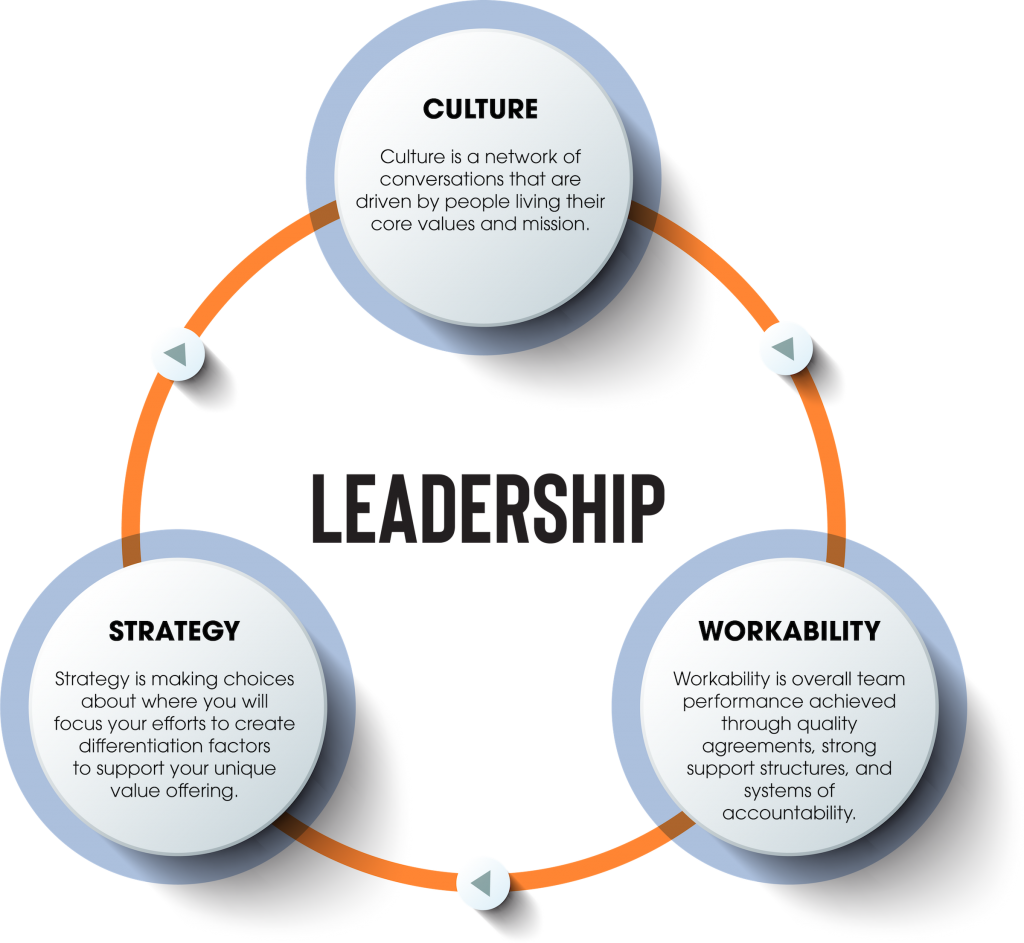
Creating a high-performance culture is not a one-pronged endeavor; meaning, there are multiple components that contribute to HP cultures.
CULTURE
What is culture and how does an organization create one?
Culture is built through a network of intentionally designed conversations that are agreed to and lived through shared values, attitudes, standards, beliefs, and practices.
Culture dictates behaviors, attitudes, how people interact with each other, what is expected, and how a company operates. It is the foundation within the organization for how the organization will perform work and the structure within the organization to build from.
Culture includes:
- Agreements – Requests/Promises
- Integrity – the ability to honor your word
- Support Structures – having the necessary equipment, processes, skills, and competencies to complete your work
- Culture of Leadership – action-oriented language
- Accountability – tracking, monitoring, counting
- Practices – there are common practices that people engage in
Culture starts at the top, then trickles down as the team observes Senior Leaders walking the talk and living the culture.
In Forbes, showed the importance of Senior Leadership in defining culture.
Forbes – Change your leaders to change your culture
“What is your organization’s biggest obstacle to transform your culture in response to market change and disruption? Forty percent responded that day to day decisions that are made to pay the bills, but undermine the stated strategy to change the culture. 24% was a lack of coherent vision for the future.”
If you’re a Senior leader who would like to get a pulse on your organization’s current culture the fastest way to do this is by listening. Listen to the current conversations happening between colleagues, what are people talking about, and what is the tone of those conversations – positive or negative?
If you like what you hear, encourage and expand those conversations. If you don’t like what you hear, start new conversations.
WORKABILITY – The Missing Link!
The term workability is not common in most organizations.
Although the elements of workability are vital, they are usually so embedded in an organization that no one really stops to think about “how” all the work is getting done and whether it is getting done effectively and efficiently with happy and satisfied workers.
Workability is all about people (conversations), processes (steps to completion), systems (ways of getting things done) and structures (equipment, tools).
It is a silence but critical piece of the HP Organization puzzle. Workability shows up in everyday life when the day to day works smoothly or is a daily challenge.
Workability is when that conference room projector works as it should when IT returns your call promptly, and when the printer rarely shuts down. All of these things create a high level of workability. A lack of workability is when there is miscommunication that leads to errors, the WIFI is sketchy and cannot be depended on for meetings, or when the processes and systems in place are outdated.
For example, in an organization, they have processes and IT structures in place that were built for a company of 100 people and are now needing to support 2,000 people. The needs of the organization have shifted, but the structures and systems in place have not changed, leading to a lack of workability.
The elements that makeup workability are often taken for granted that they will “just work”. “Just work” usually means a hardworking assistants, receptionists or other support staff has created workarounds and make-do solutions to get by and not incur additional expenses to upgrade what is needed to make things work properly.
Workability is critical for day to day operations in high-performance organizations, and it should hold a spot at the Strategic Planning table.
STRATEGY
Time to make some choices!
Strategy is often confused with planning. Planning is about creating timelines, tasks, and activities, whereas strategy is about defining what you want to do and why. What markets you will focus on, what products you will create for those markets, and which clients you want to attract. Strategy is about creating a focus and direction for what you want to achieve.
Southwest Airlines is famous for their strategic focus on low-cost airfare. Co-Founder and CEO, Herb Kelleher has spoken to the organization’s extreme discipline with their strategy and how he responds to customers that request perks that other airlines are providing.
“Southwest Airlines doesn’t do that. Maybe somebody else does, but we don’t. It greatly facilitates the operation of the company.”
Leadership Challenge:
Be intentional this week about noticing the level of workability in your life and how it affects your performance.